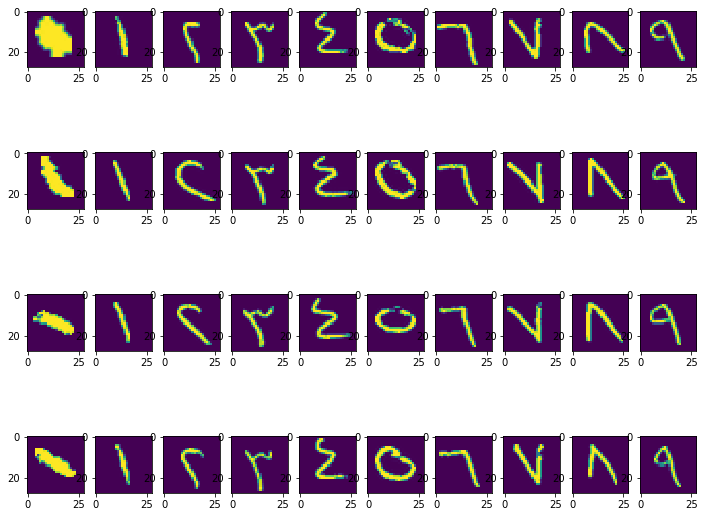Recognizing Handwritten Arabic Digits with CNN
Recognizing Handwritten Arabic Digits with CNN
The task of recognizing handwritten digits is a well-established and important research area in both machine learning and deep learning. While significant research efforts have been dedicated to recognizing handwritten digits in the English language (e.g., using the MNIST dataset), handwritten Arabic digits recognition has received comparatively less attention.
In this project, I developed a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model aimed at classifying handwritten Arabic digits, focusing on improving accuracy and performance. The dataset used for this task was the MADBase dataset, which is the Arabic equivalent of the famous MNIST dataset.
Dataset: MADBase
- The MADBase dataset consists of 60,000 handwritten Arabic digits for training and 10,000 digits for testing.
- It is widely used for evaluating models in the Arabic handwritten digits recognition domain, offering a robust platform for model training and testing, similar to MNIST but tailored for Arabic script.
The Model: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
I implemented a CNN architecture, which is known for its effectiveness in image recognition tasks due to its ability to capture spatial hierarchies in images. The network was designed and optimized to handle the variations and complexities of handwritten Arabic digits, which differ significantly from Latin digits in both form and style.
Demo Application
Live Demo: Try a Demo
Key Results
- The CNN model achieved an accuracy of 99.35% on the MADBase testing set, which is a state-of-the-art result among currently published models that utilize this dataset.
- This level of accuracy demonstrates the potential for further applications of deep learning techniques in Arabic handwritten digit recognition.
Challenges & Future Work
While the results are promising, there are still challenges in extending the model to real-world applications where more complex handwriting or noisy data may be present. Future work could explore:
- Data augmentation to handle more variations in handwriting.
- Transfer learning approaches using models pre-trained on larger datasets.
This project contributes to the growing body of research in Arabic handwriting recognition, and the model’s high accuracy highlights the potential of CNNs in addressing the unique challenges of Arabic script.