Chest X-ray Pneumonia Detection Using a Weighted Classifier
Chest X-ray Pneumonia Detection Using a Weighted Classifier
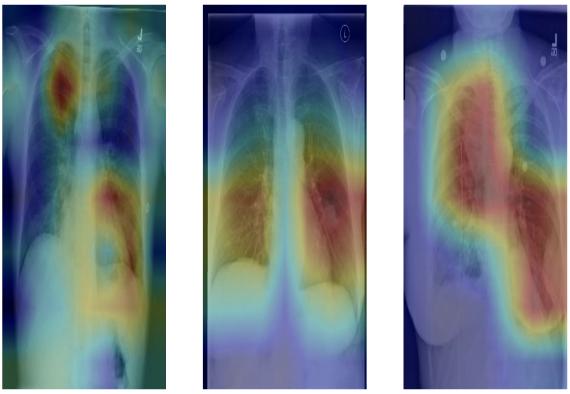
Pneumonia is a leading cause of mortality, claiming the lives of around 700,000 children each year and affecting 7% of the global population. Early and accurate diagnosis is critical in preventing deaths, and chest X-rays are the primary tool used for diagnosis. However, the task of examining chest X-rays is challenging, even for experienced radiologists, leading to a need for improved diagnostic accuracy through machine learning.
In this project, I developed an efficient model for detecting pneumonia using digital chest X-ray images. The model is designed to assist radiologists by providing a high-accuracy, AI-based diagnostic tool.
The Proposed Model: Weighted Classifier
The key contribution of this project is the introduction of a weighted classifier, which optimally combines the predictions from several state-of-the-art deep learning models:
- ResNet18
- Xception
- InceptionV3
- DenseNet121
- MobileNetV3
This novel approach enhances the overall predictive performance by leveraging the strengths of each individual model. The weighted classifier aggregates the predictions from all models, assigning higher weights to the more accurate predictions.
Techniques Employed
Transfer Learning: I applied transfer learning to fine-tune each deep learning model. This technique helps achieve higher training and validation accuracy by utilizing pre-trained weights from models that have already been trained on large datasets.
Partial Data Augmentation: To improve the robustness of the model, data augmentation techniques were applied. This helps increase the diversity of the training dataset, ensuring the model performs well on unseen data.
Key Results
The weighted classifier outperformed all individual models and achieved:
- Test accuracy: 98.43%
- AUC (Area Under Curve) score: 99.76%
These results were obtained on the Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center pneumonia dataset, a widely used dataset for pneumonia detection research.
Impact on Radiology
The proposed model serves as a powerful decision-support tool for radiologists. By providing highly accurate predictions, it helps improve the speed and accuracy of pneumonia diagnoses, especially in environments where expert radiologists may not always be available. The model’s high AUC score indicates its ability to effectively differentiate between normal and pneumonia-affected lungs, offering a reliable second opinion.
Future Directions
Future work could involve:
- Real-time implementation in clinical settings.
- Testing the model on larger and more diverse datasets.
- Exploring the use of explainable AI (XAI) to provide radiologists with insights into the model’s decision-making process, increasing trust in AI-based diagnostic tools.
With its high accuracy and generalization capabilities, this model represents a significant step forward in improving pneumonia diagnosis through machine learning.